Perplexity AI: Заменит ли он Google? Мой опыт покупки доступа за 500 рублей
В последние три недели я почти не использую обычный поиск Google или Яндекс. Всё из-за Perplexity AI. Это поисковик с нейросетью, который понимает смысл вопроса, а не ищет по словам. Он выдает не просто список сайтов, а готовый ответ по делу, со ссылками на источники.
Звучит хорошо, но официальная подписка стоит $20 в месяц. А в интернете её можно купить всего за 500 рублей на год (можно купить на Яндекс маркете, ggsel, plati и прочих серых площадках). В чём тут хитрость? Посмотрим, что это за программа, откуда такая низкая цена и есть ли смысл её покупать.
Что такое Perplexity и как он работает?
Проще говоря, Perplexity — это смесь поисковика и чат-бота типа ChatGPT. Работает он не так, как обычный поиск:
Вы пишете вопрос обычными словами. Программа понимает, что вы хотите узнать.
Perplexity быстро ищет в интернете, выбирая подходящие сайты.
Искусственный интеллект собирает найденные сведения и делает из них один ясный ответ.
Вы видите готовый текст со ссылками на сайты, откуда взята информация. Это главное удобство — можно легко всё проверить.
Можно спрашивать дальше, чтобы уточнить детали. Программа помнит ваш разговор и продолжает его.
Практический пример:
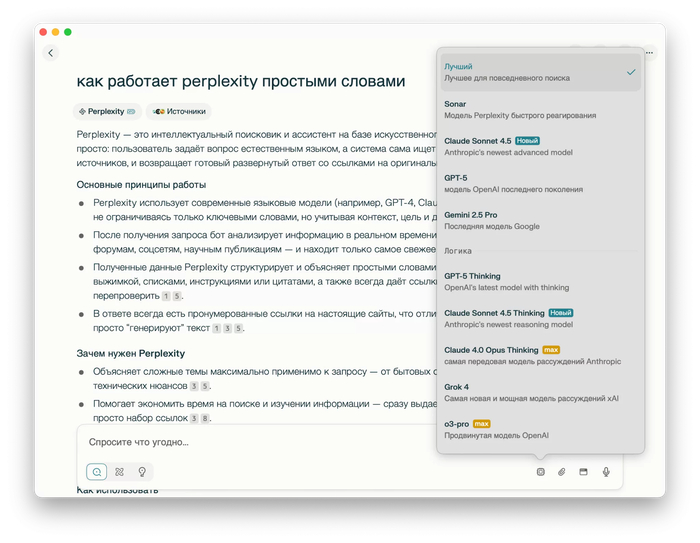
Например, я спросил «как работает perplexity простыми словами»:
Вместо списка сайтов я получил готовый ответ. Это сберегло мне очень много времени. Мне не нужно открывать сайты (хотя при необходимости я могу это сделать). Так же это не нейро-ответ Яндекса, перплексити гораздо умнее (на мой взгляд).
Официальная цена vs «Серый рынок»: в чем подвох?
Официальная подписка Perplexity Pro стоит $20 в месяц (или $200 за год). С ней вы получаете доступ к лучшим нейросетям (GPT-5, Claude 4.5, Grok и т.п.), можете загружать сколько угодно файлов и делать больше запросов.
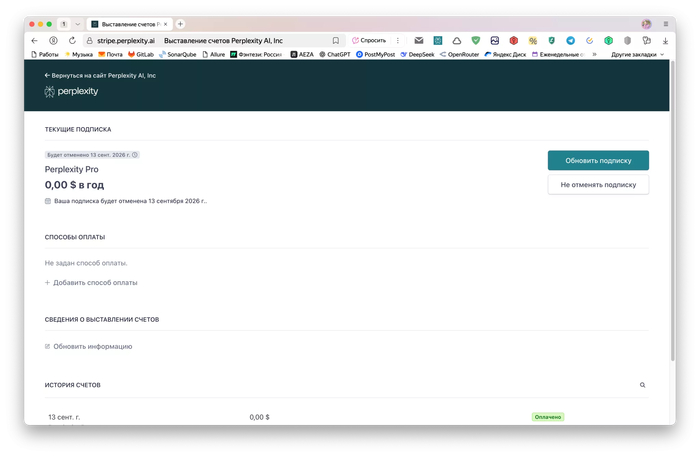
Но на серых сайтах то же самое предлагают купить за 500 рублей в год. Как так? Не понятно… Я так и не понял, но в личном кабинете указана цена подписки как $0 и все регистрируется на мою почту официально и на год. Возможно, какие-то акции самого перплексити, но это — большой вопрос конечно. В чем подвох я так и не понял.
Мой опыт и минусы Perplexity
Я рискнул и три недели назад купил такой доступ для простых личных дел. Пока всё работает хорошо. К удобству быстро привыкаешь: искать сведения для блога или узнавать о новых технологиях стало намного быстрее.
Но кроме опасностей при покупке, у самой программы есть большой минус: скрытые команды. Неизвестно, как Perplexity меняет наш вопрос перед тем, как отправить его нейросети. Он может что-то убрать или добавить от себя, и это может изменить точность ответа. Чтобы это выяснить, нужно делать детальное сравнение с работой нейросетей напрямую. Я этого пока не делал, но было бы интересно провести такой анализ.
С другой стороны, стоит ли это считать минусом?
Выводы
Одно могу сказать точно: Perplexity — это очень мощная и полезная программа, которая может поменять сам подход поиска информации в интернете: то, как мы ищем сведения / факты. А потом это, возможно, может эволюционировать дальше, в персонального помощника.
Что думаете? Кто пробовал Perplexity?